| [1]Vo N,Niedernhofer LJ,Nasto LA,et al.An overview of underlying causes and animal models for the study of age-related degenerative disorders of the spine and synovial joints.J Orthop Res.2013;31(6):831-837. [2]Capeci CM,Turchiano M,Strauss EJ,et al.Osteochondral allografts: applications in treating articular cartilage defects in the knee. Bull Hosp Jt Dis.2013;71(1):60-67. [3]张永涛,金丹.组织工程骨软骨复合体构建的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(9):1120-1124. [4]Lim HC,Bae JH,Song SH,et al.Current treatments of isolated articular cartilage lesions of the knee achieve similar outcomes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(8): 2261-2267. [5]Kelly TA,Roach BL,Weidner ZD,et al.Tissue-engineered articular cartilage exhibits tension-compression nonlinearity reminiscent of the native cartilage.J Biomech. 2013;46(11): 1784-1791. [6]Gardner OF,Archer CW,Alini M,et al.Chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28(1):23-42. [7]Schwarz S,Koerber L,Elsaesser AF,et al.Decellularized cartilage matrix as a novel biomatrix for cartilage tissue- engineering applications. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012; 18(21-22):2195-2209. [8]Cheng H,Byrska-Bishop M,Zhang CT,et al.Stem cell membrane engineering for cell rolling using peptide conjugation and tuning of cell-selectin interaction kinetics. Biomaterials. 2012;33(20):5004-5012. [9]刘清宇,王富友,杨柳.关节软骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2012, 26(10):1247-1250. [10]李元城,张卫国,秦建华,等.微流控芯片上胰岛素样生长因子1和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对兔关节软骨细胞增殖的影响[J].解放军医学杂志, 2013, 38(6):476-480. [11]Fortier LA, Barker JU, Strauss EJ, et al. The role of growth factors in cartilage repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469 (10):2706-2710.[12]Kwon DR, Park GY, Lee SU. The effects of intra-articular platelet-rich plasma injection according to the severity of collagenase-induced knee osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. Ann Rehabil Med. 2012;36(4):458-465.[13]Lee HR, Park KM, Joung YK, et al. Platelet-rich plasma loaded hydrogel scaffold enhances chondrogenic differentiation and maturation with up-regulation of CB1 and CB2. J Control Release. 2012;159(3):332-337.[14]Kon E, Buda R, Filardo G, et ai. Platelet-rich plasma: intra-articular knee injections produced favorable results on degenerative cartilage lesions. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;518(4):472-479.[15]Gobbi A, Karnatzikos G, Mahajan V, et al. Platelet-rich plasma treatment in symptomatic patients with knee osteoarthritis: preliminary results in a group of active patients. Sports Health. 2012;4(2): 162-172.[16]Filardo G, Kon E, Buda R, et al. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular knee injections for the treatment of degenerative cartilage lesions and osteoarthritis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011;19(4):528-535.[17]Kon E, Mandelbaum B, Buda R, et al. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular injection versus hyaluronic acid viscosupplementation as treatments for cartilage pathology: from early degeneration to osteoarthritis. Arthroscopy. 2011;27(11): 1490-1501.[18]熊小龙, 伍亮, 相大勇, 等.富血小板血浆对大鼠跟腱断裂早期愈合的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2012,26(4):466-471.[19]Milano G, Deriu L, Sanna PE,et al. Repeated platelet concentrate injections enhance reparative response of microfractures in the treatment of chondral defects of the knee: an experimental study in an animal model. Arthroscopys. 2012;28(5):688-701.[20]Seixa CI,Soler C,Carillo JM,et al. Effect of autologous platelet-rich plasma on the repair of full-thickness articular defects in rabbits. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arflirosc. 2013;21(8):1730-1736.[21]Zhu Y,Yuan M,Meng HY,et al. Basic science and clinical application of platelet-rich plasma for cartilage defects and osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(11):1627-1637.[22]Andia I,Maffulli N. Platelet-rich plasma for managing pain and inflammation in osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013;9(12): 721-730.[23]Filardo G,Kon E,Pereira RM,et al. Platelet-rich plasma intra-articular injections for cartilage degeneration and osteoarthritis: single- versus double-spinning approach. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(10):2082-2091.[24]Abrams GD,Frank RM,Fortier LA,et al. Platelet-rich plasma for articular cartilage repair. Sports Med Arthroscs. 2013; 21(4):213-219.[25]Chang KV,Hung CY,Aliwarga F,et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma Injections for Treating Knee Joint Cartilage Degenerative Pathology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 95(3):562-575.[26]Dold AP,Zywiel MG,Taylor DW,et al. Platelet-rich plasma in the management of articular cartilage pathology: a systematic review. Clin J Sport Med. 2014;24(1):31-43. |
.jpg)
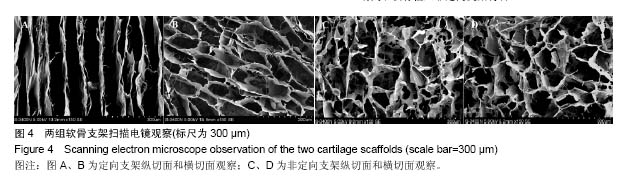
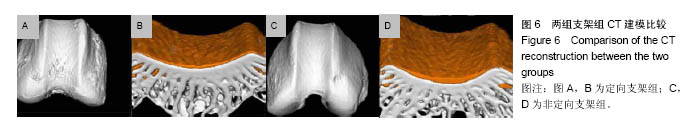
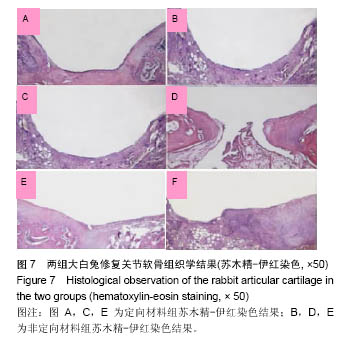
.jpg)
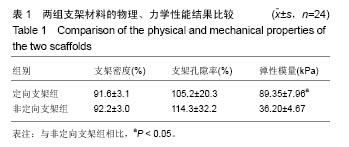
.jpg)
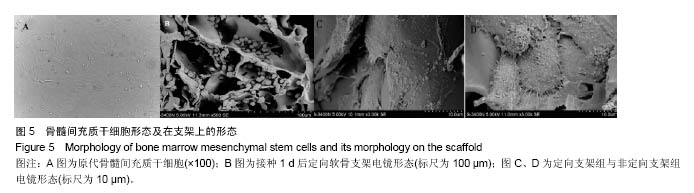
.jpg)
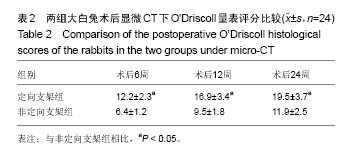
.jpg)